- diffusion is one of the proof of the particle theory of matter.
- the definition of diffusion.
- diffusion in solid, liquid and gas
- factors that affect the rate of diffusion and the related experiments.
What is Diffusion?
1. Diffusion is a process of spreading of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
2. It occurs when the particles of the substance move through the space between the particles of another substance.
3. Figure below shows how the bromine particles diffuse into the air.

4. Diffusion occurs in solid, liquid and gas.
5. The rate of diffusion is highest in gas and lowest in solid.
6. Diffusion is the proof of the particle theory of matter.
- The rate of diffusion is highest in gas and lowest in solid.
- Diffusion is the proof of the particle theory of matter.
Diffusion in Solid
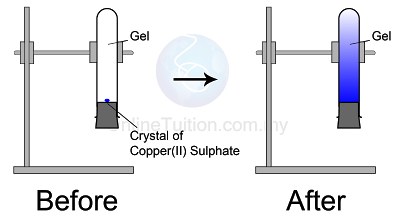 |
| Diffusion in Solid |
The blue colour of copper(II) sulphate fills up the entire test tube after a few days
- Copper(II) sulphate crystals are made of copper(II) ions and sulphate ions which are tiny and discrete.
- The particles in the copper(II) sulphate crystal will separate to become ions and diffuse randomly upwards until the whole agar turns blue.
Diffusion in Liquid
 |
| (Diffusion in Liquid) |
- Diffusion has taken place in the liquid.
- The rate of diffusion of the particles in water is faster than the diffusion rate of particles in solid.
- The occurrence of diffusion proves that potassium permanganate(VII) consist of tiny and discrete particles.
Diffusion in Gas
 |
| (Diffusion in Gas) |
- Bromine vapour is made of tiny and discrete molecules that move randomly to fill up space.
- Bromine vapour moves randomly and diffuses in all directions in air from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
The rate of diffusion is highest in gas and lowest in solid.
Video 1 – Diffusion
Video 2 – Diffusion in Solid
Video 3 – Diffusion in Liquid and Gas
Diffusion of Gases | The Fuse School
Interesting Video
Brownian Motion
 |
- Brownian motion is the physical phenomenon that tiny particles immersed in a fluid move about randomly.
- A fluid can be a liquid or a gas.
- Brownian movement, an example of diffusion, supports the kinetic theory of matter.
- Examples of Brownian movement are
- movement of smoke particles in air
- movement of pollen grains in water


