Question 3:
A student investigated the effect of oxidation of pear slices in different solutions as shown in Diagram 3.
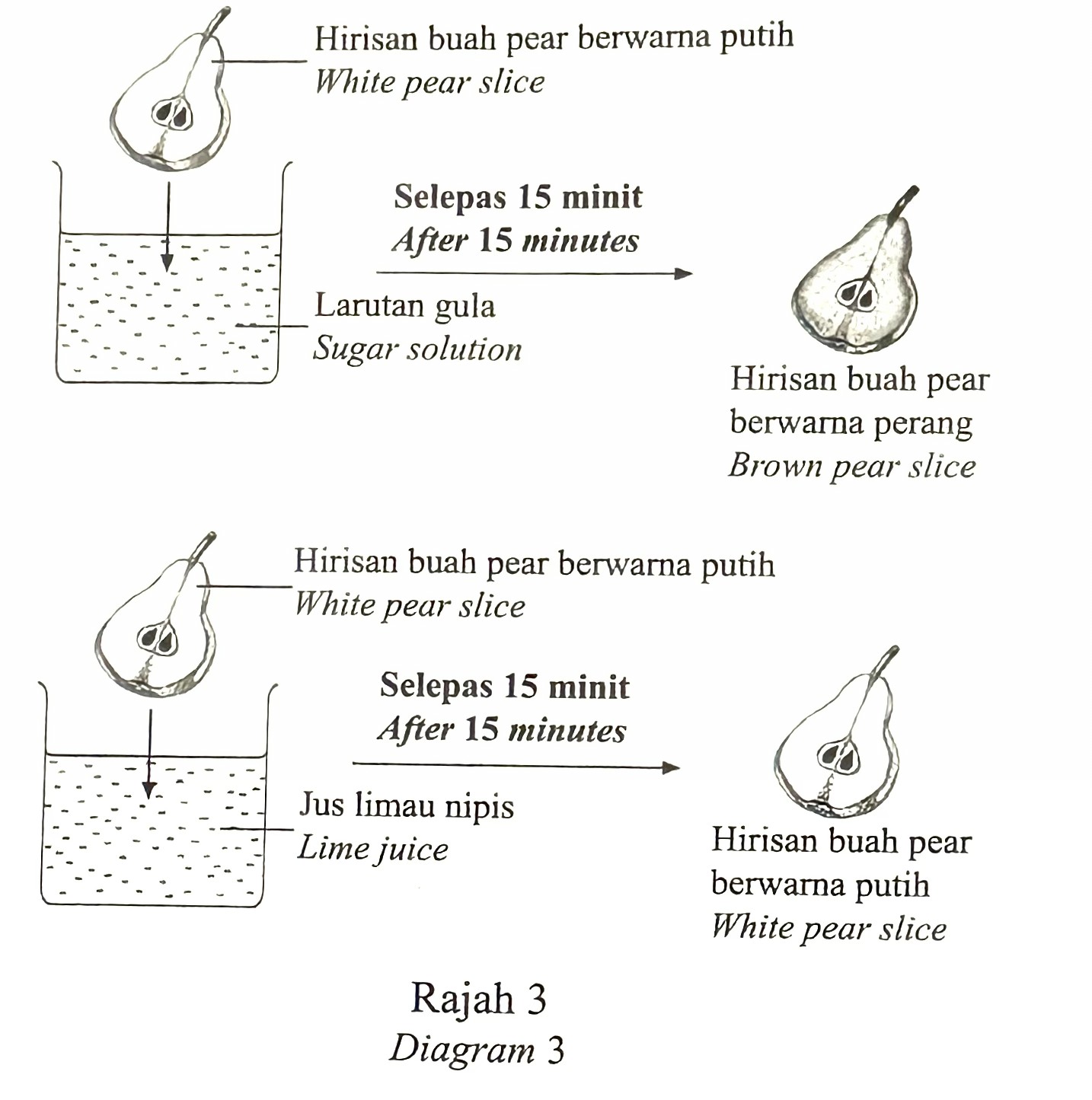
(a) Based on the experiment in Diagram 3,
(i) state one responding variable [1 mark]
(ii) state one way to control the variable in 3(a)(i) [1 mark]
(iii) state the operational definition for oxidation process of pear slice from the aspect of what is observed and what is done [1 mark]
(iv) state one conclusion. [1 mark]
(b) The student prepares a control set by putting a slice of pear into a beaker without any solution at the beginning of experiment. State the function of the control set in this experiment.
State the function of the control set in this experiment. [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) The colour of pear slices after soaking in the solution and leaving it exposed to air for 15 minutes
Explanation:
In this experiment, the colour change of pear slices shows the effects of oxidation occurring in different solutions. This shows that colour is a variable that responds to oxidation.
(a)(ii) Observing the colour condition of both pear slices soaked in two different solutions (sugar solution and lime juice) after being exposed to air for 15 minutes.
Explanation:
By observing both pear slices at the same time, we can ensure that any colour change is due to the solution used and not influenced by other factors.
(a)(iii) The process of oxidation of pear slices is the process of changing the colour of pear slices from white to brown after soaking in a sugar solution for 15 minutes.
Explanation:
This statement clearly indicates the change that occurs due to oxidation, and the specified time provides a precise context for measuring the effect of the solution on the pear slices.
(a)(iv) Lime juice can prevent the oxidation of pear slices (antioxidant solution), while sugar solution does not prevent it (not an antioxidant solution).
Explanation:
Lime juice is an antioxidant solution that slows down the oxidation reaction.
(b) To show the colour change of pear slices that occurs naturally due to oxidation without any solution.
Explanation:
A control set helps compare the effects of a solution (such as a sugar solution or lime juice) to the original condition without any solution, so we can determine whether the solution actually prevents or slows down oxidation.
A student investigated the effect of oxidation of pear slices in different solutions as shown in Diagram 3.

(a) Based on the experiment in Diagram 3,
(i) state one responding variable [1 mark]
(ii) state one way to control the variable in 3(a)(i) [1 mark]
(iii) state the operational definition for oxidation process of pear slice from the aspect of what is observed and what is done [1 mark]
(iv) state one conclusion. [1 mark]
(b) The student prepares a control set by putting a slice of pear into a beaker without any solution at the beginning of experiment. State the function of the control set in this experiment.
State the function of the control set in this experiment. [1 mark]
Answer:
(a)(i) The colour of pear slices after soaking in the solution and leaving it exposed to air for 15 minutes
Explanation:
In this experiment, the colour change of pear slices shows the effects of oxidation occurring in different solutions. This shows that colour is a variable that responds to oxidation.
(a)(ii) Observing the colour condition of both pear slices soaked in two different solutions (sugar solution and lime juice) after being exposed to air for 15 minutes.
Explanation:
By observing both pear slices at the same time, we can ensure that any colour change is due to the solution used and not influenced by other factors.
(a)(iii) The process of oxidation of pear slices is the process of changing the colour of pear slices from white to brown after soaking in a sugar solution for 15 minutes.
Explanation:
This statement clearly indicates the change that occurs due to oxidation, and the specified time provides a precise context for measuring the effect of the solution on the pear slices.
(a)(iv) Lime juice can prevent the oxidation of pear slices (antioxidant solution), while sugar solution does not prevent it (not an antioxidant solution).
Explanation:
Lime juice is an antioxidant solution that slows down the oxidation reaction.
(b) To show the colour change of pear slices that occurs naturally due to oxidation without any solution.
Explanation:
A control set helps compare the effects of a solution (such as a sugar solution or lime juice) to the original condition without any solution, so we can determine whether the solution actually prevents or slows down oxidation.