Change in Heat and Kinetic Energy of Particles
1. The change in temperature will influences the kinetic energy or the speed of the motion of the particles.
2. When a substance is heated, the kinetic energy of the particles in the substance increases. This causes the particles to move or vibrate faster.
3. Likewise, when a substance is cooled, the kinetic energy of the particles in the substance decreases. This causes the particles to move or vibrate slower.
4. The kinetic energy of the particles in a substance is directly proportional to the temperature of the substance.
Inter-conversion between States of Matter
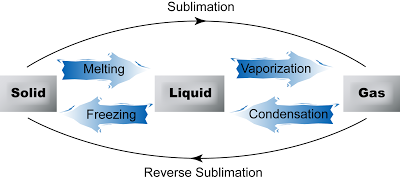
| Melting |
Definition
Melting is the process where a solid changes to its liquid state at a certain temperature (called the melting point) and pressure when it is heated.
Notes
- When a solid is heated, the particles obtain energy and vibrate at a faster rate.
- As the temperature increases, the vibration of the particles increases until they reach the melting point where the particles obtain enough energy to overcome the forces that hold them in their fixed positions.The solid then changes into a liquid.
- During melting, the temperature remains constant. This is because the heat energy is taken in by the particles to overcome forces between them instead of being used to raise the temperature.
- The freezing and melting points of a pure substance are the same.
|
| Freezing |
Definition
Freezing is the process where a liquid changes to its solid state at a certain temperature (called freezing point) and pressure when it is cooled.
Notes
- When a liquid is cooled, the temperature drops as heat energy is released to the surroundings.
- As heat energy is released, the kinetic energy of the particles in the liquid decreases, causing a slower movement of particles.
- The particles lose their energy and are pulled closer by the strong forces between the particles.
- As the temperature keep on dropping until it reach the freezing point, the liquid start changing into solid.
- The temperature stays constant while the liquid freezes because heat energy is released when the particles slow down to take up fixed and orderly positions in the solid.
|
Vaporization
(Evaporation) |
Definition
Vaporization, also called evaporation is the process whereby atoms or molecules in a liquid state gain sufficient energy to enter the gaseous state.
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid at a certain temperature (the boiling point) and pressure when heat is applied to it.
Notes
Evaporation
- Evaporation occurs below the boiling point of the liquid.
- The particles escape from the surface of the liquid to form gas.
- Evaporation differs from boiling in that it only takes place at the surface of the liquid and it is very slow.
- On the other hand, boiling takes place throughout the liquid and is very fast.
- Factors influencing rate of evaporation
- Humidity of the air.
- Temperature of the substance.
- Flow rate of air.
- Inter-molecular forces. The stronger the forces keeping the molecules together in the liquid or solid state the more energy that must be input in order to evaporate them.
- If conditions allow the formation of vapour bubbles within a liquid, the vaporization process is called boiling.
Boiling
- When a liquid is heated, the particles gain energy and move faster.
- As heat energy is keep on supplying to the liquid, the particles will eventually obtain enough energy to completely break the forces in between molecule.
- The liquid then changes into a gas and particles are now able to move freely and are far apart.
- The temperature at which this happens is called the boiling point.
- The temperature remains constant during boiling because heat energy that is absorbed by the particles is used to break the forces holding them together.
|
| condensation |
Definition
Condensation is the process by which a gas or vapor changes to liquid state at certain temperature and pressure when it is cooled.
Notes
- When a gas is cooled, the particles lose kinetic energy.
- As a result they move slower and this will cause the forces between them grow stronger.
- At this point, the gas changes into liquid.
- During condensation, heat is given out to the surroundings.
- Condensation can occur at or below the boiling point of the substance
|
| sublimation |
Definition
Sublimation is a process of conversion of a substance from the solid to the vapour state without its becoming liquid.
Notes
- Some solids change directly into gas without becoming a liquid.
- This process is called sublimation.
- When heated, the particles of the solid gain enough energy to break the forces between them and move freely as a gas.
- When cooled, the gas changes straight back to solid.
- Examples of substances which sublime are solid carbon dioxide (dry ice), ammonium chloride and iodine.
|
Interesting Video:
Inter-conversion Between the 3 States of Matter

